The Historical Significance of https://piraminds.com/
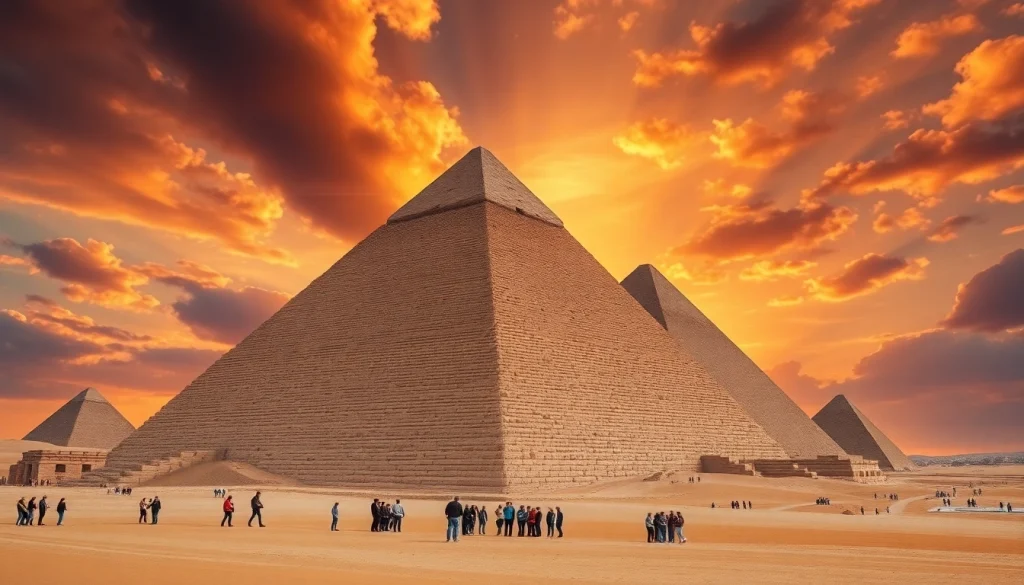
The pyramids of Egypt are not only an architectural wonder but are also steeped in rich history that has captivated the world for centuries. Their grandeur and engineering precision reflect the ancient Egyptian civilization’s cultural and social dynamics. Understanding the significance of https://piraminds.com/ is essential to grasp the complex layers that comprise their historical importance.
The Origins of the Pyramids
The history of Egyptian pyramids dates back to the Third Dynasty of the Old Kingdom, around 2630 BCE. The first pyramid, known as the Step Pyramid of Djoser, located in Saqqara, represented a significant leap from the simple mastaba tombs that preceded it. This architectural innovation was designed by the famous architect Imhotep, marking a pivotal moment in the construction and use of monumental structures in ancient Egypt. Pyramids were not merely funerary monuments; they symbolized the pharaoh’s promised journey to the afterlife, reflecting their divine status.
The Role of Pharaohs
The central figures behind the pyramids were the pharaohs, who were considered living gods on Earth. These monarchs believed that their rule extended beyond death, necessitating extravagant burial sites that would ensure their immortality. Each pyramid served as a tomb and a religious center, facilitating rituals and offerings meant to appease the gods on behalf of the deceased. The grandeur of the pyramids thus not only showcased the individual power of the pharaoh but also stressed the community’s belief in the divine order and the afterlife. Pharaonic authority was closely tied to their burial practices, and the construction of these monuments was a testament to their power and the societal organization of labor and resources.
Cultural Impact on Ancient Egypt
The cultural significance of the pyramids goes beyond their physical presence. They encapsulated the complexities of Egyptian religion, art, and societal norms. Pyramids are intricately linked with burial practices and the belief in resurrection. The interior chambers often contained elaborate hieroglyphics and wall paintings that told the story of the deceased’s life and their journey in the afterlife. These art forms not only served religious purposes but also provided insight into the socio-political landscape of the time. Thus, the pyramids became symbols of national identity, influencing subsequent generations and cultures within and beyond Egypt.
Architectural Marvels: Understanding Design and Construction
The architectural ingenuity of the Egyptian pyramids continues to astonish modern engineers and architects. These structures were built to last for millennia, showcasing advanced engineering techniques and understanding of material properties.
Architectural Techniques Used in https://piraminds.com/
Pyramids were constructed using a process that involved precise planning and an understanding of geometry. The famous Giza pyramids utilized a square base and a triangular design, which is structurally stable. Techniques such as aligning the pyramids with celestial bodies demonstrated the Egyptians’ advanced knowledge of astronomy. Construction involved comprehensive surveying methods to ensure level bases and precise angles, which would have required skilled labor and advanced mathematical understanding.
Materials and Workforce Behind the Pyramids
The materials used in the construction of the pyramids predominantly consisted of limestone, sandstone, and granite. Limestone blocks were quarried locally, while finer quality stone was transported from distant quarries. The logistics of transporting heavy stones across land and water were a monumental task, demanding organized labor. Estimates suggest that tens of thousands of workers, including skilled laborers, craftsmen, and support personnel, were involved in the construction process. Contrary to popular belief, these workers were likely not slaves but rather paid laborers, evidenced by the discovery of workers’ villages, offering insights into their living conditions and organization.
Innovations in Ancient Engineering
The construction of pyramids necessitated innovative solutions to various engineering challenges, including moving massive stones and maintaining structural integrity. The Egyptians developed techniques such as sledging, where workers pulled stone blocks on sleds over lubricated paths to reduce friction. Innovations in ramp construction showcased their problem-solving abilities in lifting heavy materials to great heights. These advancements laid the groundwork for future architectural endeavors, influencing diverse cultures worldwide.
Exploration and Discoveries in Egyptology
Egyptology as a discipline has evolved significantly, driven by the desire to unveil the mysteries surrounding the pyramids and ancient Egyptian civilization.
Major Archaeological Findings
Archaeological explorations have revealed a wealth of information about the pyramids, including hidden chambers and structural innovations. Noteworthy discoveries, such as the intact burial chambers and intricate passages, have provided invaluable insights into ancient Egyptian funerary practices and daily life. Recent findings, including unexplored shafts and geological features beneath the pyramids, continue to generate interest and prompt new theories regarding their construction and purpose.
The Impact of Technology on Research
The integration of modern technology into Egyptology has transformed research methodologies. Ground-penetrating radar and 3D scanning techniques allow archaeologists to investigate subsurface features without intrusive excavations. This has accelerated the discovery process, revealing hidden aspects of the pyramids and associated structures. The application of these technologies enhances our understanding of ancient engineering capabilities and the socio-cultural significance of these monuments.
Understanding the Artifacts Found in Pyramids
Artifacts discovered within the pyramids, such as canopic jars, jewelry, and ceremonial items, provide insights into the beliefs, customs, and daily life of ancient Egyptians. These objects were intended to accompany the deceased into the afterlife, reflecting the importance attributed to life after death in their culture. Analyzing these artifacts enables historians and archaeologists to piece together the intricate tapestry of ancient Egyptian reality and belief systems.
Pyramids in Popular Culture and Their Legacy
The fascination with pyramids extends into modern popular culture, influencing art, literature, and media.
The Symbolism of Pyramids in Media
Pyramids inspire various forms of expression, symbolizing mystery, power, and timelessness. They appear in films, books, and artworks, often representing the allure of ancient civilizations. This symbolism transcends cultures, evoking a sense of wonder and curiosity about human history and achievement. Their portrayal in popular media continues to captivate audiences, reinforcing their status as icons of ancient knowledge and civilization.
Influence on Modern Architecture
The architectural principles utilized in pyramid construction have inspired countless modern designs. Notable skyscrapers and monuments reflect attributes of pyramid geometry and proportions. The strategic importance of light, space, and form evident in pyramid structures is evident in contemporary architecture. Innovations from ancient Egyptian design continue to resonate, bridging past accomplishments with modern techniques and philosophies.
Tourism and Economic Impact
Pyramids are central to Egypt’s tourism industry, attracting millions of visitors annually. The economic impact of pyramid-related tourism is substantial, contributing to local and national economies. Tourism generates revenue through entry fees, guided tours, and associated businesses. However, the influx of visitors also poses challenges, including the preservation of these ancient sites in the face of increasing human activity. Sustainable tourism practices are becoming paramount to protect Egypt’s cultural heritage for future generations.
FAQs About the Pyramids
What are the Pyramids of Giza?
The Pyramids of Giza, located in Egypt, are ancient monumental tombs built for Pharaohs during the Fourth Dynasty of the Old Kingdom. They are among the most iconic and well-preserved structures from ancient Egypt.
How were the pyramids built?
The pyramids were constructed using massive stone blocks, with sophisticated techniques for transportation, lifting, and precise measurements. Labor involved thousands of skilled workers, not slaves, who contributed to this monumental endeavor.
What purposes did the pyramids serve?
Pyramids served primarily as royal tombs for pharaohs, embodying their beliefs in the afterlife. They also functioned as ceremonial centers, facilitating rituals for the deceased and showcasing royal power.
Who were buried in the pyramids?
The pyramids primarily housed the remains of Pharaohs and their consorts. They also contained offerings, artifacts, and provisions intended for the deceased’s journey in the afterlife.
Can tourists visit the pyramids?
Yes, the Pyramids of Giza are open to tourists. Visitors can explore the sacred sites, experience guided tours, and admire the architectural wonders while taking part in cultural education on ancient Egypt.